
Posted On : Nov 28 2020
Unveiling Hamas
Hamas, an acronym for Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiya (Islamic Resistance Movement), is a Palestinian political and militant organization that has elicited both staunch support and vehement criticism on the global stage.
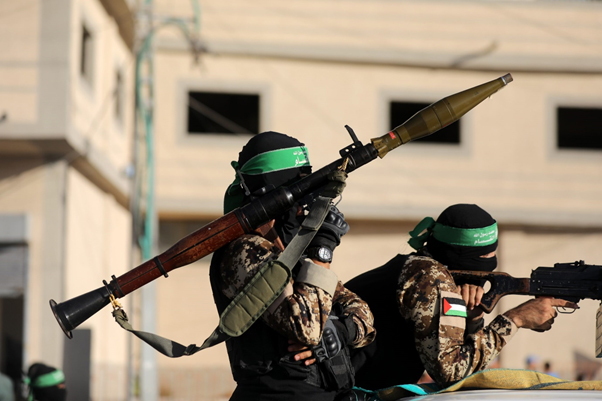

Established in 1987 during the First Intifada, Hamas has since evolved into a multifaceted entity that plays a significant role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. This article delves into the origins, ideology, activities, and broader implications of Hamas' presence in the Middle East.
Origins and Ideology
Hamas emerged from the crucible of Palestinian resistance against Israeli occupation. Born during a time of intense Palestinian frustration and anger, the movement's founding principles melded political activism, social welfare, and armed resistance. Rooted in a blend of Palestinian nationalism and Islamism, Hamas seeks to establish an independent Palestinian state that encompasses the entirety of historical Palestine, rejecting the existence of Israel.
Activities and Strategies
Hamas employs a combination of military and political strategies to advance its objectives. Its military wing, the Izz al-Din al-Qassam Brigades, has engaged in a series of conflicts with Israel, often resorting to tactics such as suicide bombings and rocket attacks. On the other hand, the organization's political arm has participated in Palestinian governance through elections, most notably winning the 2006 legislative elections in the Gaza Strip.
Social Services and Popularity
Hamas has garnered significant popular support by providing social services and addressing the needs of Palestinians, particularly in the Gaza Strip. Its schools, hospitals, and charities offer vital services that often fill gaps left by governmental institutions. This dual role, as a resistance movement and a social services provider, further complicates international responses to Hamas.
International Reactions
Hamas' designation as a terrorist organization by numerous countries, including the United States and the European Union, reflects the global community's concerns about its violent tactics and refusal to recognize Israel's right to exist. This designation has substantial implications for the group's international interactions and access to funding.
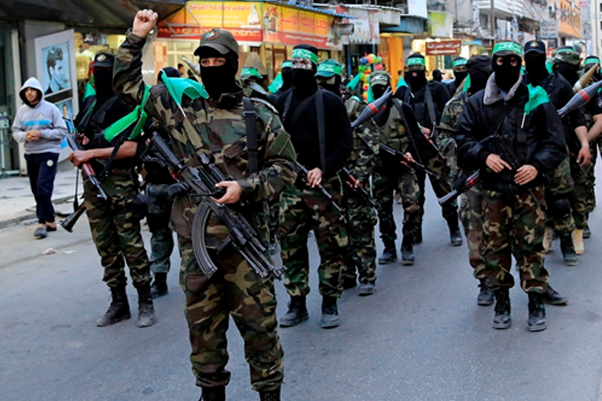

Hamas' presence has significantly shaped the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. While the organization's resistance efforts resonate with many Palestinians who view it as a legitimate defender of their rights, its violent tactics have hindered diplomatic efforts and peaceful coexistence. The frequent flare-ups of violence between Hamas and Israel, including recent conflicts in 2008-2009, 2012, 2014, and 2021, underscore the group's impact on regional stability.
Challenges and Controversies
Hamas faces a myriad of challenges, both internally and externally. Internally, the organization grapples with governance complexities and maintaining public support while juggling its dual roles. Externally, Hamas navigates international pressure, regional dynamics, and the ongoing Israeli military presence in Palestinian territories.
Conclusion
Hamas remains a central figure in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, stirring heated debates and complex geopolitical dynamics. While its strategies and objectives are divisive, the group's widespread support within Palestinian communities is a testament to the deeply rooted grievances and aspirations of the Palestinian people. As the region continues to grapple with challenges, the path forward must address the broader issues that underpin Hamas' appeal, seeking avenues for negotiation, reconciliation, and a just resolution to the long-standing conflict.





















ragi3
Nice Article by Ananth Ragi