
Nikita Bohra
Posted On : Sep 4 2020
China`s Digital Silk Road: Unraveling the Technological Ambitions
While the traditional Silk Road facilitated physical trade and cultural exchange, the Digital Silk Road seeks to achieve a comparable impact by leveraging technology and digital connectivity.
The "Digital Silk Road" is an integral component of China's ambitious Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a colossal infrastructure and economic development project aimed at enhancing connectivity and fostering economic cooperation across Asia, Europe, Africa, and beyond. This article delves into the key aspects of China's Digital Silk Road, its objectives, challenges, and its implications for participating countries and the global digital landscape.
Understanding the Digital Silk Road
The Digital Silk Road is a strategic initiative by the Chinese government to extend its influence in the digital realm and promote the export of Chinese technologies and digital infrastructure to other countries. It focuses on bolstering digital connectivity, fostering e-commerce, building smart cities, promoting 5G networks, and advancing digital financial services.
The project aims to create a vast network of digital infrastructure that facilitates the seamless flow of information, e-commerce transactions, and technological innovations between China and participating countries.
Objectives of the Digital Silk Road
Technological Export: The Digital Silk Road provides China with a platform to export its advanced technologies, including 5G, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and smart city solutions, to countries along the BRI routes. This enhances China's standing as a global technology leader and strengthens its presence in emerging markets.
Economic Cooperation: By enhancing digital connectivity, the initiative aims to promote economic cooperation and trade between China and participating nations. It fosters cross-border e-commerce, facilitates supply chain integration, and encourages investment and joint ventures in the digital sector.
Infrastructure Development: The Digital Silk Road seeks to address the digital divide in developing countries by promoting the construction of digital infrastructure. This includes building undersea cables, data centers, and improving internet connectivity to enable access to digital services and technologies.
Cultural and Educational Exchange: The initiative emphasizes fostering cultural and educational exchanges through digital platforms. This includes promoting online language learning, virtual classrooms, and digital content sharing to facilitate cross-cultural understanding.
Soft Power Projection: China sees the Digital Silk Road as a means to extend its soft power globally. By providing technological support and connectivity to other countries, China aims to enhance its image as a responsible global player and a cooperative partner.
Challenges and Criticisms
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The Digital Silk Road raises concerns over data security and privacy, as participating countries may become dependent on Chinese technology and data infrastructure, potentially leading to data breaches or surveillance risks.
Digital Divide: While the initiative aims to address the digital divide, there are concerns that the Digital Silk Road may primarily benefit countries already well-connected, leaving less developed nations behind.
Geopolitical Tensions: The project has faced criticism from some countries, particularly Western nations, who view it as a tool for China to extend its geopolitical influence and promote its vision of internet governance, which differs from the open and free model favored by Western democracies.
Debt Sustainability: Critics argue that the Digital Silk Road projects may lead to debt sustainability issues for participating countries, as the infrastructure investments often come from loans provided by Chinese financial institutions.
Lack of Transparency: Some participating countries have expressed concerns about the lack of transparency in the terms of agreements and contracts related to Digital Silk Road projects, leading to doubts about long-term implications.
Implications for Participating Countries
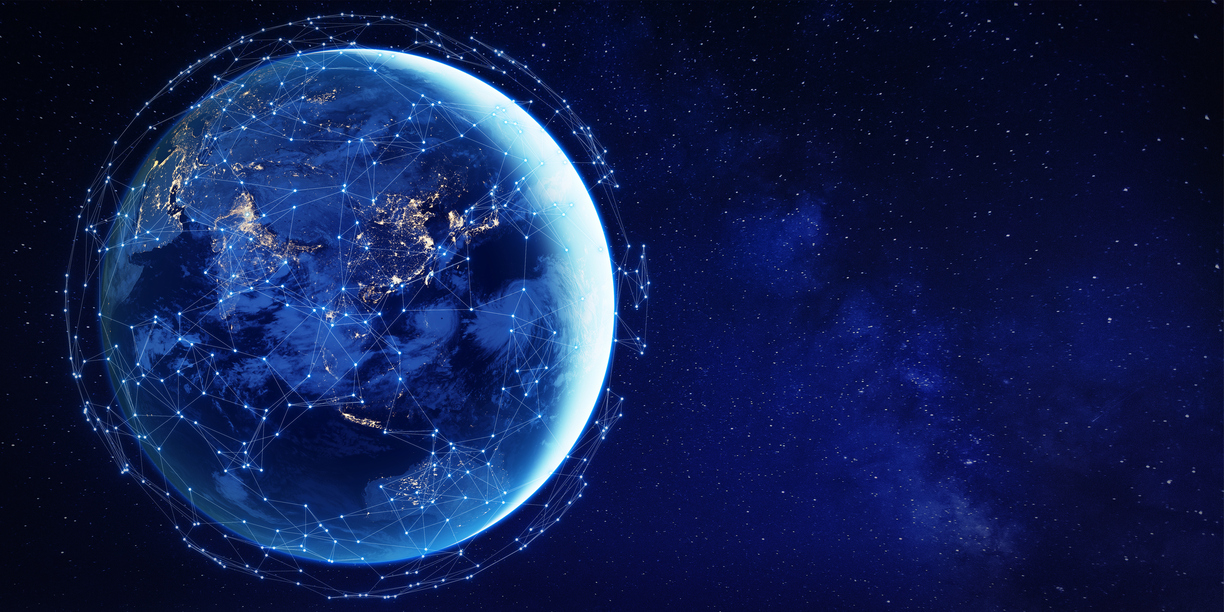

Economic Growth and Development: For many developing countries, participation in the Digital Silk Road can provide access to advanced technologies, boost economic growth, and create new business opportunities.
Enhanced Digital Connectivity: The initiative can improve digital connectivity and internet access, enabling citizens and businesses to tap into global markets and digital services.
Technological Dependence: Countries relying heavily on Chinese technologies may face challenges if there are disruptions in the supply chain or geopolitical tensions affecting technology imports.
Potential Surveillance and Control: Some critics argue that the Digital Silk Road may enable China to extend its surveillance and control capabilities beyond its borders, impacting the digital freedoms of participating countries.
Conclusion
China's Digital Silk Road represents a transformative and complex initiative aimed at reshaping the global digital landscape and enhancing technological connectivity across regions. While the project promises economic benefits and technological advancements, it also faces numerous challenges and concerns. As countries evaluate their participation in the Digital Silk Road, a delicate balance between economic gains and potential risks must be considered to ensure sustainable and mutually beneficial outcomes for all parties involved.





















ragi3
Good Article