Posted On : Dec 7 2020
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) stands as one of Iran`s most powerful and influential institutions, playing a pivotal role in the country`s political, military, and regional affairs.
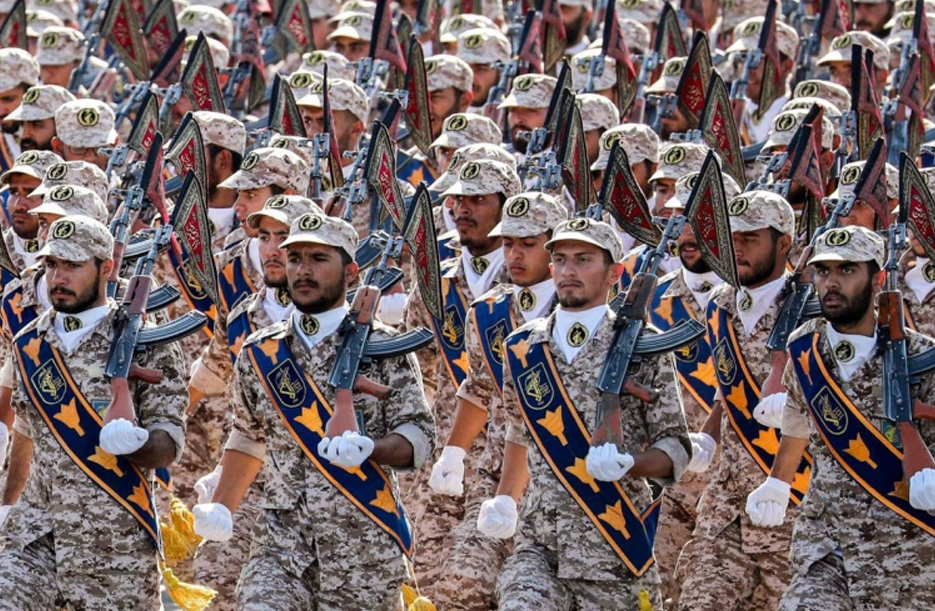

Formed in the wake of the 1979 Iranian Revolution, the IRGC has evolved into a multifaceted force with extensive capabilities that extend beyond traditional military functions. This article explores the origins, functions, and regional impact of the IRGC.
Origins and Functions
The IRGC was established shortly after the Islamic Revolution in 1979, primarily tasked with safeguarding the revolution's achievements and protecting the newly formed Islamic Republic from internal and external threats. Over time, the IRGC's influence expanded, encompassing not only military operations but also political and economic domains. The IRGC serves as a parallel military force to the regular Iranian Armed Forces, providing additional capabilities and serving as a guardian of the regime's ideology. Beyond its military role, the IRGC has significant involvement in domestic affairs, including maintaining social order and suppressing dissent. It also operates a vast economic network, controlling various sectors such as construction, telecommunications, and energy.
Regional Impact
The IRGC's influence extends well beyond Iran's borders, shaping regional dynamics in the Middle East. Through its Quds Force, a special unit responsible for extraterritorial operations, the IRGC has been instrumental in supporting various proxy groups across the region. These proxies, including Hezbollah in Lebanon, various Shiite militias in Iraq, and Houthi rebels in Yemen, have furthered Iran's interests and regional ambitions. The Quds Force's involvement in Syria's civil war, supporting the Bashar al-Assad regime, showcased the extent of the IRGC's regional influence. The group's strategic vision and operational capabilities have enabled it to establish a network of allies and proxies, effectively expanding Iran's sphere of influence across the Middle East.
Challenges and Controversies
The IRGC's expansive reach has generated both support and criticism. Domestically, it enjoys a degree of popular backing for its role in safeguarding the revolution's ideals and providing social services. However, there are segments of Iranian society that view the IRGC as a hindrance to political openness and economic reform. Internationally, the IRGC has faced accusations of supporting terrorism and destabilizing the region through its proxy activities. These allegations have led to international sanctions and tensions between Iran and various countries, particularly the United States.
Conclusion
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) remains a significant force within Iran and across the broader Middle East. Emerging from the tumultuous aftermath of the Islamic Revolution, the IRGC's multifaceted functions encompass military, political, and economic domains. Its role in regional proxy conflicts has elevated Iran's influence, while also drawing international scrutiny. As Iran navigates complex regional dynamics and global tensions, the IRGC's role continues to shape its domestic and foreign policies, casting a lasting impact on the Middle East's geopolitical landscape.
No Comments Added