Posted On : Dec 7 2020
Unraveling Jama`at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM)
Jama`at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM) is a prominent militant group operating in the Sahel region of West Africa.
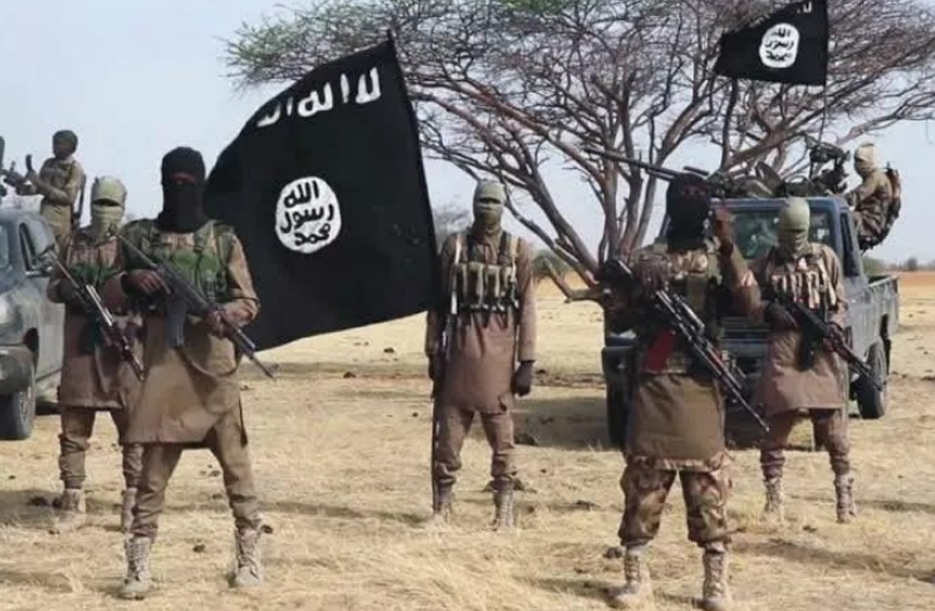

Formed in 2017 as an amalgamation of various jihadist factions, JNIM has emerged as a complex and formidable force, posing significant security challenges to the countries in the region. This article delves into the origins, objectives, activities, and regional impact of JNIM.
Origins and Formation
JNIM was established through the merger of several extremist groups, including Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), Ansar Dine, Al-Mourabitoun, and the Macina Liberation Front. Led by Iyad Ag Ghaly, a Tuareg leader, JNIM sought to consolidate jihadist efforts in the Sahel under a unified banner. The group's formation was aimed at enhancing operational capabilities, sharing resources, and projecting a more potent image.
Objectives and Ideology
JNIM's ideology is rooted in Salafi-jihadism, which seeks to establish an Islamic state based on a strict interpretation of Sharia law. The group's objectives include overthrowing governments it perceives as corrupt and collaborating with Western powers, as well as combating "foreign occupiers" in the Sahel. JNIM's activities are centered around instilling fear through acts of violence and asserting its influence over local populations.
Activities and Strategies
JNIM employs a range of tactics to achieve its goals. These tactics include ambushes, suicide bombings, kidnappings, and attacks on military and civilian targets. The group has targeted security forces, peacekeepers, and civilians, causing instability and displacement across the Sahel. JNIM's control over certain regions allows it to impose its version of Islamic law, gaining the allegiance of some communities through the provision of social services and justice systems.
Regional Impact and Challenges
JNIM's activities have had a profound impact on the Sahel region's security landscape. The group's presence exacerbates existing challenges such as poverty, governance deficits, and intercommunal tensions. The porous borders and vast ungoverned spaces in the Sahel have enabled JNIM to move fluidly and evade counter-terrorism efforts. Moreover, its collaboration with other jihadist organizations has contributed to regional instability and terrorism-linked activities.
International Response
The international community, including countries like France and the United States, has recognized the threat posed by JNIM and its associates. Efforts to counter the group include military interventions, intelligence-sharing, and capacity-building initiatives for local security forces. The G5 Sahel Joint Force, composed of troops from Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Chad, is an example of a regional response to the threat of JNIM and other militant groups.
Conclusion
Jama'at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM) stands as a complex and influential player in the Sahel's security dynamics. Formed through the merger of multiple extremist factions, the group has capitalized on regional vulnerabilities to expand its influence. While JNIM's activities remain a grave concern, efforts by regional governments and international partners seek to curb its expansion and restore stability to the Sahel. As the situation evolves, effectively addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by JNIM will require sustained collaboration, targeted strategies, and comprehensive approaches that address the root causes of extremism in the region.
No Comments Added